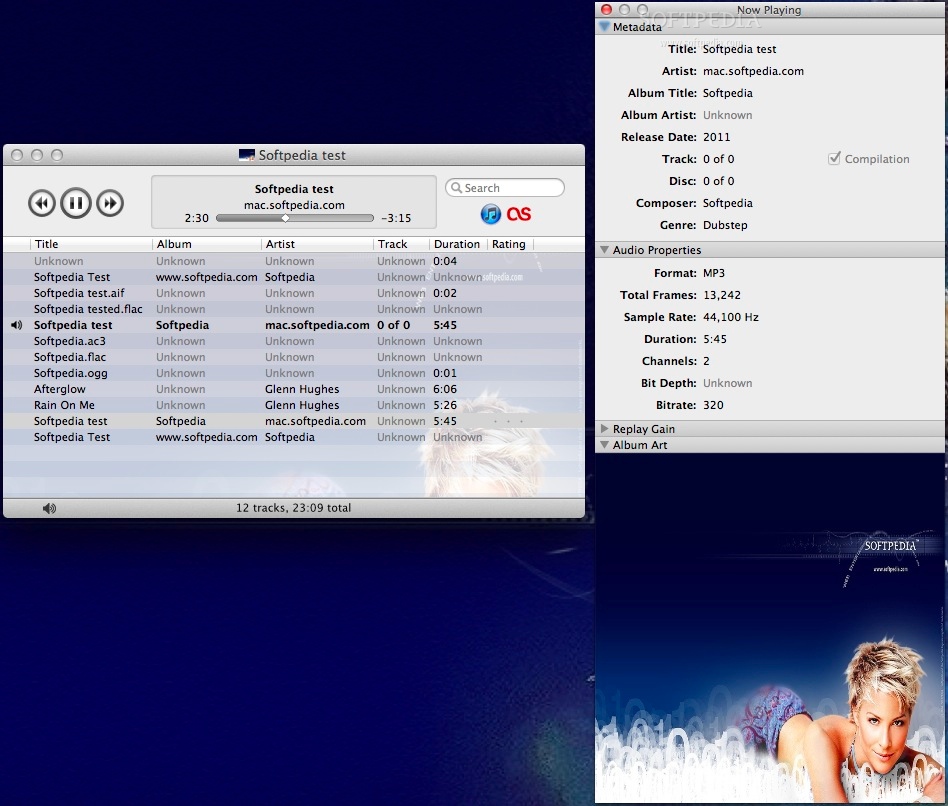
Decibel for Mac. 3,323 downloads Updated: October 23, 2018 Trial. Review Free Download specifications 100% CLEAN report malware. Minimalist and easy to use audio player for Mac OS X that offers support for a large number of audio file formats, and delivers smooth playback. The decibel (symbol: dB) is a relative unit of measurement corresponding to one tenth of a bel (B).It is used to express the ratio of one value of a power or field quantity to another, on a logarithmic scale, the logarithmic quantity being called the power level or field level, respectively.Two signals whose levels differ by one decibel have a power ratio of 10 1/10 (approximately 1.25893). Decibel Audio Player is a real audio player and does not include features that are not meant to be part of an audio player. These features, such as tagging files or burning CDs, generally have a better support in dedicated software. If you are looking for an audio player than can make coffee, then you should stay away from Decibel and give a try to other players (e.g., Amarok, Exaile). The most popular versions among Decibel for Mac users are 1.3 and 1.2. The bundle identifier for this application is org.sbooth.Decibel. Decibel.zip is the common file name to indicate this program's installer. From the developer: Decibel is an audio player tailored to the particular needs of audiophiles. Download Krisp Desktop from Mac or Windows. Speak Without Noise. With a single button, the background noise going from you to other call participants will be removed. Listen Without Noise. With a single button, the background noise coming from.
Sound travels in waves, produced when an object — such as a stereo speaker — pushes on the air around it, causing small changes in air pressure. To describe sound waves, acoustic experts refer to concepts such as frequency and amplitude.
You can easily set a Volume Limit on your iPod and iPhone. Click here to get answers to frequently asked questions about the Volume Limit.
The Science of Sound
The frequency of the waves in the sound determines the sound wave's pitch. Frequency is commonly measured in Hertz (Hz) with one Hz being equal to one wave completing a cycle per second. The human ear can detect a wide range of frequencies — from approximately 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. Amplitude is a description of the sound wave's strength. As the amplitude of a sound wave increases, the volume of the sound increases. Music consists of a mixture of different frequencies and amplitudes.
The sound level heard by your ears is commonly measured in decibels. When referring to sound, a decibel is used to measure the amplitude of the sound wave. Decibels are useful in measuring sound because they can represent the enormous range of sound levels the human ear can hear using a more manageable scale. On the decibel scale, the softest sound that can be heard is 0 dB. Each increase of 10 dB represents an approximate doubling of the perceived loudness of the sound.
Sound and Your Ears
You can hear because your ears convert the vibrations of a sound wave in the air into signals that your brain interprets as sound. When the vibrations of a sound wave enter your ear, your eardrum and a set of tiny bones in your ear (the well-known hammer, anvil, and stirrup) amplify those vibrations. In your inner ear, these amplified vibrations move tiny hair cells that then convert the vibrations into nerve impulses sent to your brain. Your brain then interprets these nerve impulses as sound.
If you expose your ears to excessive sound pressure, you can harm those small hair cells in your ears. And if harmed, those hair cells can lose the ability to transmit sound to your brain. As a result, you could experience noise-induced hearing loss. Symptoms can include distorted or muffled sound or difficulty understanding speech.
While you can experience noise-induced hearing loss as a result of a one-time exposure to an extremely loud sound — like a gunshot — noise-induced hearing loss can also occur as a result of repeated exposure to loud sounds over time.
Listen Responsibly
Most research about noise-induced hearing loss has focused on prolonged exposure to loud sounds in industrial workplaces. While not as much research exists regarding the effect of recreational exposure to loud sound, if you listen to music and audio with headphones or earbuds — whether they're connected to your iPod, your computer, or some other audio source — you should follow a few common-sense recommendations.

Think about the volume
There's no single volume setting appropriate for everyone. Ddl for mac. You may experience a different sound level with different earbuds or headphones and with different EQ settings. Some hearing experts recommend that you set the volume while in a quiet environment, turn the volume down if you can't hear people speaking near you, avoid turning up the volume to block out noisy surroundings, and limit the amount of time that you use earbuds or headphones at high volume.
Keep Track of Time
You should also pay attention to how long you listen to audio at high volume. Remember: you can adapt to higher volume settings over time, not realizing that the higher volume may be harmful to your hearing. Hearing experts warn that noise-induced hearing loss can also occur as a result of repeated exposure to loud sound over time. The louder the volume, the less time required before your hearing may be affected. If you experience ringing in your ears or hear muffled speech, stop listening and have your hearing checked.
File Maker Pro
FileMaker is probably the best known database application for the Mac. It has a feature set comparable to Microsoft Access, but with a strong focus on forms (layouts) as the primary way of accessing databases. Similar to Access, FileMaker stores your database logic and all the data in a single file. It also has some support for scripting, and offers options for publishing databases on the web.
However, it's also necessary to note that FileMaker is very different from Access. There is a strict distinction between application logic and the underlying tables in Access. In FileMaker, logic and data are more closely linked. The underlying tables are more or less hidden from the user, and not as easily accessible via SQL as in Access.
Decibel For Sound Machine

You can hear because your ears convert the vibrations of a sound wave in the air into signals that your brain interprets as sound. When the vibrations of a sound wave enter your ear, your eardrum and a set of tiny bones in your ear (the well-known hammer, anvil, and stirrup) amplify those vibrations. In your inner ear, these amplified vibrations move tiny hair cells that then convert the vibrations into nerve impulses sent to your brain. Your brain then interprets these nerve impulses as sound.
If you expose your ears to excessive sound pressure, you can harm those small hair cells in your ears. And if harmed, those hair cells can lose the ability to transmit sound to your brain. As a result, you could experience noise-induced hearing loss. Symptoms can include distorted or muffled sound or difficulty understanding speech.
While you can experience noise-induced hearing loss as a result of a one-time exposure to an extremely loud sound — like a gunshot — noise-induced hearing loss can also occur as a result of repeated exposure to loud sounds over time.
Listen Responsibly
Most research about noise-induced hearing loss has focused on prolonged exposure to loud sounds in industrial workplaces. While not as much research exists regarding the effect of recreational exposure to loud sound, if you listen to music and audio with headphones or earbuds — whether they're connected to your iPod, your computer, or some other audio source — you should follow a few common-sense recommendations.
Think about the volume
There's no single volume setting appropriate for everyone. Ddl for mac. You may experience a different sound level with different earbuds or headphones and with different EQ settings. Some hearing experts recommend that you set the volume while in a quiet environment, turn the volume down if you can't hear people speaking near you, avoid turning up the volume to block out noisy surroundings, and limit the amount of time that you use earbuds or headphones at high volume.
Keep Track of Time
You should also pay attention to how long you listen to audio at high volume. Remember: you can adapt to higher volume settings over time, not realizing that the higher volume may be harmful to your hearing. Hearing experts warn that noise-induced hearing loss can also occur as a result of repeated exposure to loud sound over time. The louder the volume, the less time required before your hearing may be affected. If you experience ringing in your ears or hear muffled speech, stop listening and have your hearing checked.
File Maker Pro
FileMaker is probably the best known database application for the Mac. It has a feature set comparable to Microsoft Access, but with a strong focus on forms (layouts) as the primary way of accessing databases. Similar to Access, FileMaker stores your database logic and all the data in a single file. It also has some support for scripting, and offers options for publishing databases on the web.
However, it's also necessary to note that FileMaker is very different from Access. There is a strict distinction between application logic and the underlying tables in Access. In FileMaker, logic and data are more closely linked. The underlying tables are more or less hidden from the user, and not as easily accessible via SQL as in Access.
Decibel For Sound Machine
Bento
Bento was the entry level database application from the makers of Filemaker. Unfortunately it has been discontinued in July 2013 and is no longer available for purchase.
Open Office / Libre Office
Open Office and Libre office include a database application that tries to mimic Microsoft Access. It is difficult to use and misses many important features, such as simple import/export tools.
SQLite (using Base)
SQLite is not a full database application like Access. There are no forms or reports in SQLite, there's only your data and a simple, fast SQL engine. SQLite is used by many applications under the hood as an internal format and therefore most interesting to application developers.
A command line utility for SQLite 3 is included with every Mac, aptly named sqlite3. Most people will however prefer working with a graphical application like the excellent Base from Menial (available on the Mac App Store). Base offers a simple interface for viewing tables (with support for images) and creating custom SQL queries.
Apple Numbers and Microsoft Excel
Numbers and Excel are spreadsheet applications and thus not a replacement for Microsoft Access. However, they have good support for working with tables. If your database consists of only few tables and no forms, these apps might just do the trick. You can at least sort and filter your tables.
Decibel For Mac
Converting Access Databases to Apple Numbers with MDB Viewer
Converting Access Databases to Microsoft Excel with MDB Viewer
Microsoft Access in Parallels / VMWare
Relational Database For Mac
If none of the above are suitable, you can always ressort to actually running Microsoft Access on your Mac using virtualisation software like Parallels Desktop or VMWare Fusion.
